A tripoint, is a geographical point at which the boundaries of three countries meet. These can be on land (dry) or demarcated by rivers or lakes (wet). Tripoints can be easy to access or isolated, they can be marked with large monuments or not easily identifiable at all. There are 48 Asian Tripoints. The challenges of visiting Asian tripoints are not only distance from the UK but that they are either disputed or in terrain which is difficult to reach. Security concerns makes visits to borders a logistical and organisational challenge.
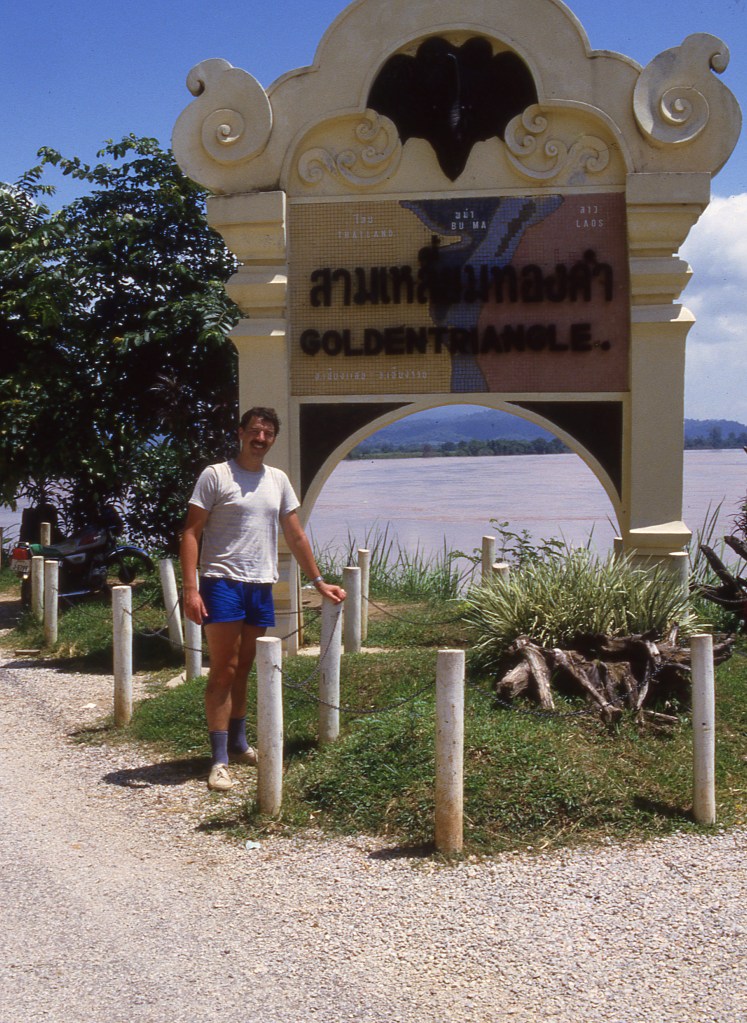

Table: Asian Tripoints
| Number | Name | Countries | coordinates | type | notes/links |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | AEOMSA | Oman – Saudi Arabia – United Arab Emirates | 22°42′30″N 55°13′E | Dry | Marked. Point established following OMSA border accord (1990) as Umm az Zumūl well. Access best from Oman. |
| 2 | AFCNPK | Afghanistan – China – Pakistan | 37°2′N 74°34′E | Dry | Isolated. At head of Wakhjir Pass, the treaty notes an unnamed peak (5630m) Easternmost point of AF. |
| 3 | AFCNTJ | Afghanistan – China – Tajikistan | 37°14′N 74°53′E | Dry | At or near the Peak Povalo Shveikovski (5054m) |
| 4 | AFIRPK | Afghanistan – Iran – Pakistan | 29.8610°N 60.8828°E | Dry | The tripoint is located at the summit of Kuh-i-Malik Salih mountain (1635m) it is a trekkable summit. Possible BM#186. |
| 5 | AFIRTM | Afghanistan – Iran – Turkmenistan | 35°37′N 61°17′E | Dry | The tripoint is located on the Tedzhen river. Situated about 2km north of Zulfikar pass on thalweg in the dry former bed. Possible indirect BM#001 AFSU |
| 6 | AFTJUZ | Afghanistan – Tajikistan – Uzbekistan | 37°10′N 67°47′E | Wet | The tripoint is located in the Amu Darya river. Possible indirect BM#107/1 AFSU |
| 7 | AFTMUZ | Afghanistan – Turkmenistan – Uzbekistan | 37°21′N 66°33′E | Both | The tripoint is located in the Amu Darya river. Remote & inhospitable area. Possible indirect BM#91/2 AFSU |
| 8 | AMAZGE | Armenia – Azerbaijan – Georgia | 41°18′07″N 45°00′14″E | Dry | Unclear, possible location is the Babakyar mountain on a ridge near saddle just southwest of the summit, however encroachment by AZ complicates things. |
| 9 | AMAZIRe | Armenia – Azerbaijan – Iran (east) | 38°52′N 46°32′E | Wet | The tripoint is located in the Aras river, in line with the Meghri Ridge (AM). BM#35 IRSU. |
| 10 | AMAZIRw | Armenia – Azerbaijan – Iran (west) | 38°51′N 46°9′E | Wet | The tripoint is located in the Aras river in line with the Zangezur ridge (AM). |
| 11 | AMAZTR | Armenia – Azerbaijan – Turkey | 39°43′N 44°46′E | Wet | The tripoint is located in the Aras river. BM#04 SUTR. |
| 12 | AMGETR | Armenia – Georgia – Turkey | 41°8′N 43°28′E | Dry | The tripoint is at the secondary summit of Mount Erakatar. BM#148 SUTR 1926. Ascent, due to the closed Armenian-Turkish border, is not allowed without prior agreement with the border guards. The nearest villages are Shaghik and Garnarich. |
| 13 | AZGERU | Azerbaijan – Georgia – Russia | 41°54′00″N 46°24′07″E | Dry | The tripoint is located at Pereval Machkhalroso pass (2790m) in the Caucasus Mountains |
| 14 | AZIRTR | Azerbaijan – Iran – Turkey | 39°38′N 44°49′E | Wet | Disputed. The tripoint is located in the Aras river at its confluence with the Kara river. BM#1 IRSU. |
| 15 | BDINMM | Bangladesh – India – Myanmar | 21°58′N 92°36′E | Dry | Tin Mukh located on Teen Matha (876m). Access from Sepru Para village. Guides recommended. Marked by a pillar with names and flags of the respective countries. |
| 16 | BTCNINe | Bhutan – China – India (east) | 27°46′N 91°39′E | Dry | Disputed. Isolated high altitude point in the Himalayas. Tawang district in Arunachal Pradesh is adjacent to the border and tripoint area. |
| 17 | BTCNINw | Bhutan – China – India (west) | 27°20′N 88°55′E | Dry | Disputed. Doklam Plateau dispute. The tripoint is located just north of Mount Gipmochi (4427m). China claims Gipmochi as the China–India–Bhutan tri-junction point. Bhutan and India, however, claim that the tri-junction is 6.5 km to the north, at Batang La. |
| 18 | CNINMM | China – India – Myanmar | 28°13′N 97°21′E | Dry | Disputed. Diphu Pass is agreed by CNMM however IN believe the tripoint should be 5km further north on the watershed. Diphu Pass lies on the McMahon Line line. |
| 19 | CNINNPe | China – India – Nepal (east) | 27°53′0N 88°8′0E | Dry | The tripoint is possibly located on the summit of Jongsang peak (7463m). This is highest tripoint in the world. The Nepalese believe the tripoint is at Jhinsang Chuli (6164m) 27°50′10N 88°12′30E |
| 20 | CNINNPw | China – India – Nepal (west) | 30°12′0 N 81°02′0 E | Dry | Disputed. Both India and Nepal claim the Kalapani area, currently under Indian juristiction. The tripoint is possibly located near the Tinkar Pass at the watershed between Mapchu & Kali river & its Tinkar tributary. The Nepalese believe the tripoint is located at Limpiyadhura (5516m). 30°25′10 N 80°30′15 E. Map 1 |
| 21 | CNINPK | China – India – Pakistan | 35.6°N 76.8°E | Dry | The tripoint is located about a kilometre southeast of the Sia Kangri summit (7422m) in the Karakoram. Territories on all sides are disputed. The land immediately to the southwest of the peak is claimed by both Pakistan and India and controlled by Pakistan. The land to the northeast is part of the Trans-Karakoram Tract, controlled by China under a 1963 border agreement with Pakistan but is claimed by India. The land to the southeast is claimed by Pakistan and India, but controlled by India, as a part of Ladakh. |
| 22 | CNKGKZ | China – Kyrgyzstan – Kazakhstan | 42°13′N 80°10′E | Dry | High altitude and remote. The tripoint is located on a secondary summit of Khan Tengri at 6637m. Khan Tengri (6995m) is the highest point in Kazakhstan and third-highest peak in Kyrgyzstan. Map |
| 23 | CNKGTJ | China – Kyrgyzstan – Tajikistan | 39°28′N 73°36′E | Dry | Tripoint is located on the summit of Kurumdy 1 Mountain (6614m). Map |
| 24 | CNKPRU | China – North Korea – Russia | 42°25′N 130°38′E | Wet | The tripoint is located in the Tumin river at the intersection the North Korea–Russia and China–North Korea borders that run along the middle of the Tumen River with the China–Russia border that approaches the junction point overland from the north. The principal border treaty was signed on April 17, 1985. The 3 countries have tripoint monuments on their respective banks. Interpretation of various treaties may mean that a China–North Korea border zone exists in the river forming a condominium meaning the tripoint technically is not located there. Krogh (2011) |
| 25 | CNKZRU | China – Kazakhstan – Russia | 49.0998°N 87.3123°E | Dry | The tripoint is located on a ridge junction 8km east of an unnamed remote peak. |
| 26 | CNLAMM | China – Laos – Myanmar | 21°34′N 101°9′E | Wet | The tripoint is located in the Upper Mekong or Lancang River where it intersects with the CNLA border. Direct CNLA BM# 45 on left bank & indirect CNMM BM#245 on right bank |
| 27 | CNLAVN | China – Laos – Vietnam | 22°24′N 102°9′E | Dry | The tripoint is located on Khoang La San Mountain. There is an impressive monument. |
| 28 | CNMNRUe | China – Mongolia – Russia (east) | 49°50′42.3″N 116°42′46.8″E | Dry | The tripoint is marked by the border monument called Tarbagan-Dakh and is accessible via access roads. Marker is elevated above salt marsh on stilts. |
| 29 | CNMNRUw | China – Mongolia – Russia (west) | 49°10′13.5″N 87°48′56.3″E | Dry | The tripoint is located at the summit of Nairamdal Peak or Friendship Peak (4,082 m) which is the one of five peaks of the Tavan Bogd mountains. |
| 30 | EGILJO | Egypt – Israel – Jordan | 29°25’24″N 34°55’49″E | Wet | The tripoint is located in the Gulf of Aqaba. At the Gulf’s northern end lie three major cities, Eilat in Israel, Taba in Egypt and Aqaba in Jordon. |
| 31 | EGILPS | Egypt – Israel – Palestine | 31°13′N 34°16′E | Dry | The modern land boundary between Israel and Egypt was confirmed in a 1979 Peace Treaty. The tripoint is located at the SE corner of the Gaza strip. |
| 32 | EGJOSA | Egypt – Jordan – Saudi Arabia | 29°23’17″N 34°54’26″E | Wet | The tripoint is located in the Gulf of Aqaba approximately 18 kms due south of the Jordanian port of Aqaba. |
| 33 | ILJOSY | Israel – Jordan – Syria | 32°45′N 35°45′E | Wet | Disputed. The precise location of the tripoint is at present unclear owing to the Israeli occupation of the Golan Heights, which are claimed by Syria. The de jure tripoint lies immediately east of the Israeli town of Sha’ar HaGolan, whereas the de facto tripoint lies at the border’s junction with the United Nations UNDOF Zone south-east of Metzar. |
| 34 | ILJOPSn | Israel – Jordan – Palestine (north) | 32°23′N 35°33′E | Wet | Disputed. In 1994, the West Bank was officially separated from Jordan as part of the Israel-Jordan peace treaty. Israel maintains full control over 60 percent of the area, with some roads that only Israelis can use and checkpoints that restrict the movements of Palestinians. The Israeli West Bank barrier has been built along the green line. The tripoint is at the northern end. |
| 35 | ILJOPSs | Israel – Jordan – Palestine (south) | 31°30′N 35°29′E | Wet | Disputed. See above. The tripoint is at the southern end. |
| 36 | ILLBSY | Israel – Lebanon – Syria | 32°45′N 35°45′E | Dry | The precise location of the Lebanese–Israeli–Syrian tripoint is unclear due to Israel’s occupation of the Golan Heights stemming from the 1967 Six-Day War. The de jure tripoint lies on the Hasbani River, a tributary of the river Jordan, at 33.24 22°N 35.62 44°E, just north-east of the Israeli town of Ma’ayan Baruch. The de facto tripoints lie on the tripoint(s) with the United Nations UNDOF Zone. The situation is further complicated by the dispute over the Shebaa farms area on the Golan-Lebanon border. |
| 37 | IQIRTR | Iran – Iraq – Turkey | 37°9′N 44°47′E | Dry | The tripoint is marked by BM#125/12 at the source of the Hajji Bak river. Approximately 2km south of the Dalamper summit. |
| 38 | IQJOSA | Iraq – Jordan – Saudi Arabia | 29°6′N 46°33′E | Dry | The tripoint is located at hill Jabal ‘Anazah (1010m). |
| 39 | IQJOSY | Iraq – Jordan – Syria | 33°22′N 38°48′E | Dry | The tripoint is located close to the USAF base at Tanf and the Al Waleed Border Crossing JOSY. |
| 40 | IQKWSA | Iraq – Kuwait – Saudi Arabia | 29°6′N 46°33′E | Dry | The tripoint is located where the IQSA border intersects with the Wadi al-Batin river. Marked by IQKW BM#1 1993 & later IQSA BM#1 |
| 41 | IQSYTR | Iraq – Syria – Turkey | 37.1116°N 42.3633°E | Wet | The tripoint is located at the confluence of Tigris river and Little Khabur river. |
| 42 | KGKZUZ | Kyrgyzstan – Kazakhstan – Uzbekistan | 42°16′N 70°57′E | Dry | The tripoint is located in the Ugam Range near the summit of Mount Chatangat (4163m). Possibly SW of the actual summit. |
| 43 | KGTJUZ | Kyrgyzstan – Tajikistan – Uzbekistan | 40°14′N 70°59′E | Dry | The tripoint is located in the Fergana Valley |
| 44 | KHLATH | Cambodia – Laos – Thailand | 14°20’33″N 105°12’23″E | Wet | Located at the Col de Preah Chambot in the Chaine des Dangrek mountains). |
| 45 | KHLAVN | Cambodia – Laos – Vietnam | 14°41′N 107°33′E | Dry | The tripoint is located on a 1000m hill hat rises from in Vietnam’s Kon Tum province, Lao’s Attapu province, and Cambodia’s Rattanakiri province. A border marker was erected in 2007 and the spot is now a tourist attraction. Access is via the Bo Y border crossing. |
| 46 | KZTMUZ | Kazakhstan – Turkmenistan – Uzbekistan | 41°19′N 56°0′E | Dry | The tripoint is located on the Ustyurt Plateau. |
| 47 | LAMMTH | Laos – Myanmar – Thailand | 20°21′N 100°5′E | Wet | The famous Golden Triangle tripoint is located at the confluence of the Kok and Mekong rivers. Today, the Thai side of the river confluence, Sop Ruak, has become a tourist attraction. It is possible to take boat trips on the river and cross to Don Sao and another tourist attraction on Laos side. |
| 48 | OMSAYE | Oman – Saudi Arabia – Yemen | 18°59’57″N 52°0’12″E | Dry | The tripoint is located within the barren Rub’ al Khali desert, marked by a concrete block. North of the Mazyonah Border crossing (OM). |

Supplementary information including treaties and maps Details here or click on the image above
Maps of Asian Tripoints
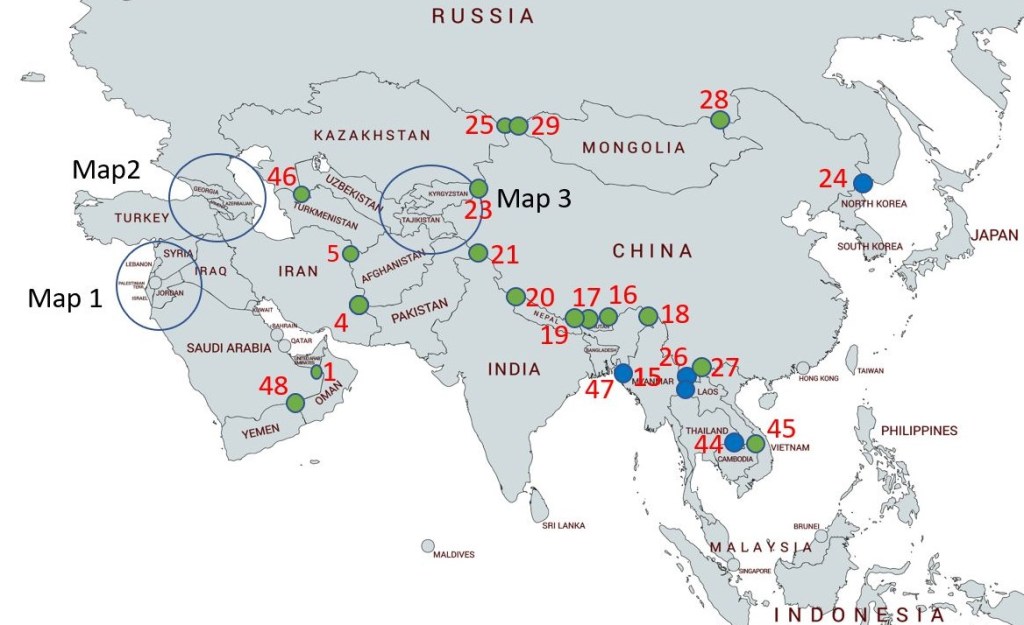
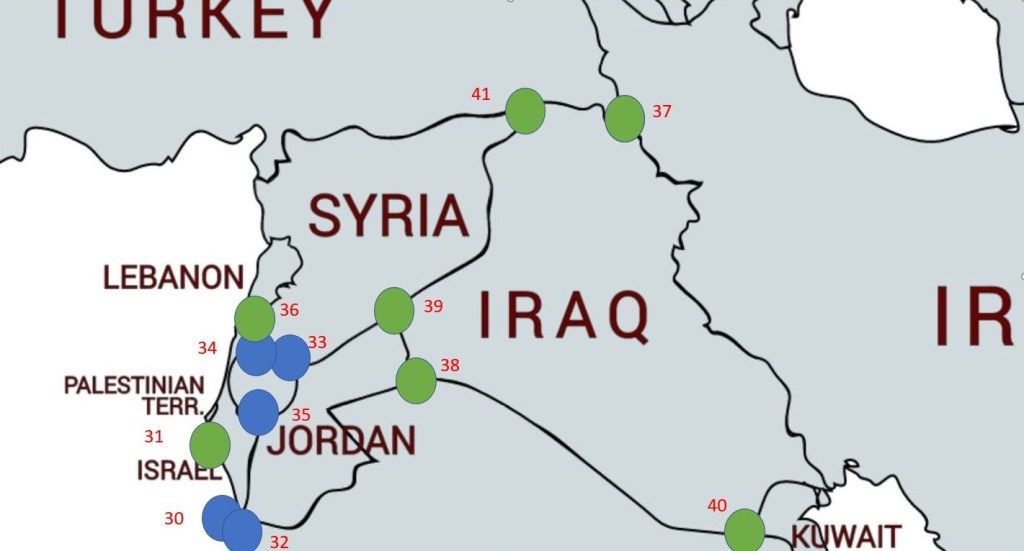
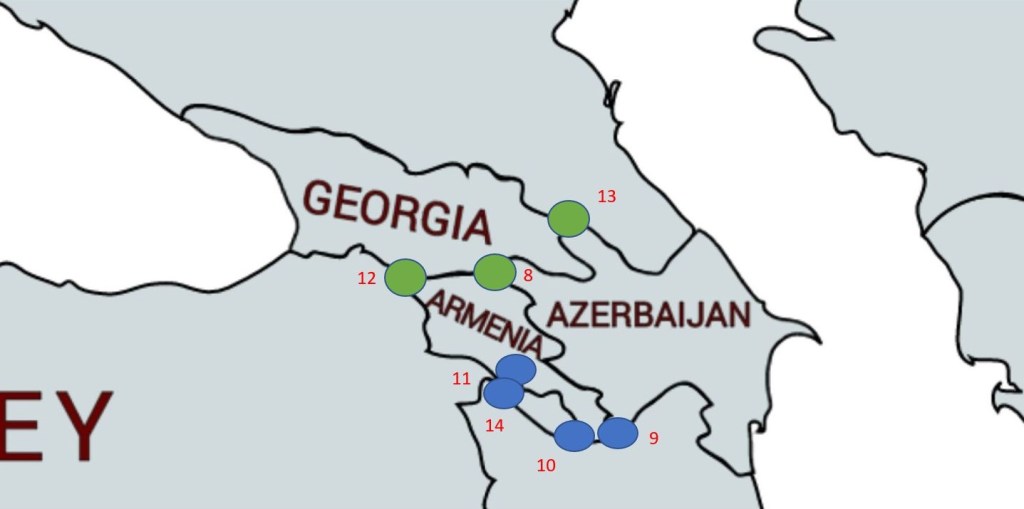
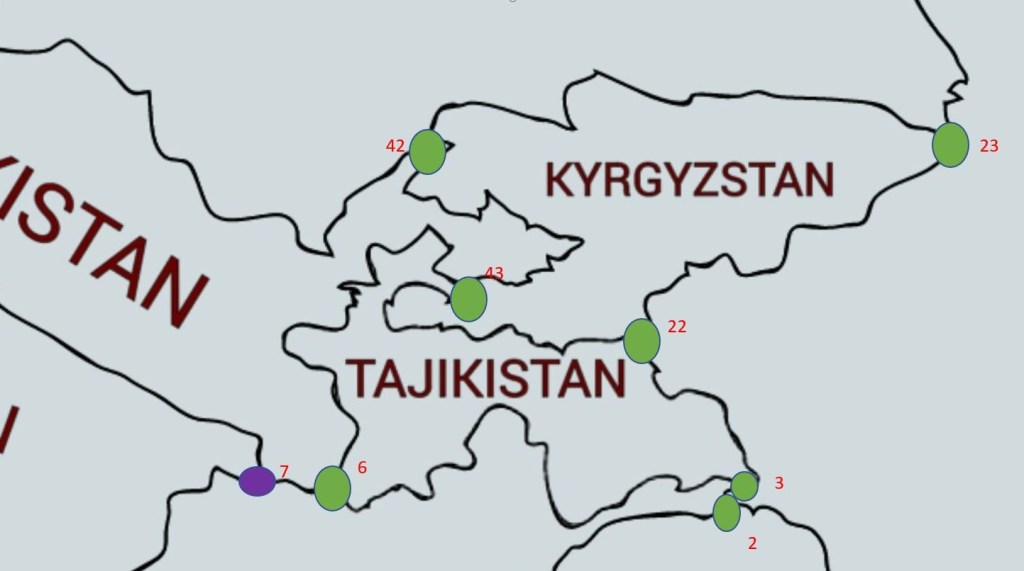
Tripoint Visit Classes
The table below attempts to classify a tripoint visit into a number of classes. Could you touch the actual spot where the countries join? If so that is a Class A, a visit to a wet tripoint is almost always a Class C. Some monuments such as FINOSE the tripoint between Finland – Norway and Sweden is too large to touch the stone on the top, hence a Class B. Not everyone uses this classification and it is offered here as a bit of fun to stimulate discussion.
| TRIPOINT VISIT CLASSES | |
|---|---|
| Class A | Touched |
| Class B | Basically there. Successful attempt to reach wet tripoint by wading, swimming or canoeing. Very close to a dry tripoint but unable to touch due to a physical barrier/obstacle. |
| Class C | Within 500m, visible |
| Class D | Distant. visible |
| Class E | Tripoint area visited but Tripoint not observed. |
| Source: Acroorca (2002) Published on Boundarypoint 12/07/2003 Edited Arnold (2024). |
My Tripoint Gallery (1 out of 48 visited so far)
The International Standard for country codes and codes for their subdivisions is ISO 3166 this allocates a 2 letter designation to each country. When identifying a tripoint it is necessary to collate the 3 country codes in alphabetical order, hence the tripoint between Laos, Myanmar and Thailand becomes LAMMTH. The US and Canada often use 2 letters to denote states and provinces e.g. Alabama AL which is technically incorrect as all sub national territories according to ISO 3166 should have the initial 2 letter country designation followed by up to 3 further letters. Alabama ought therefore be US- AL. Delaware has the same 2 letter code as Germany: DE which has the potential for confusion.
Please click on the photos below to access the reports of my visits, or the red highlighted text above.
Site Navigation
In order to find your way around the site, either click on the links (text in red) or use the menus at the top of the page. About leads you to the country pages, with links to individual borders. The about menu leads you to my visit reports by country.
Mobile Advice
Tables display correctly when holding your mobile horizontally.
To access the links to other pages please click on the 3 horizontal dots at the bottom of the page.

Great list and very helpful for us to build our Border Tripoints on NomadMania site… Check us out 🙂
LikeLike