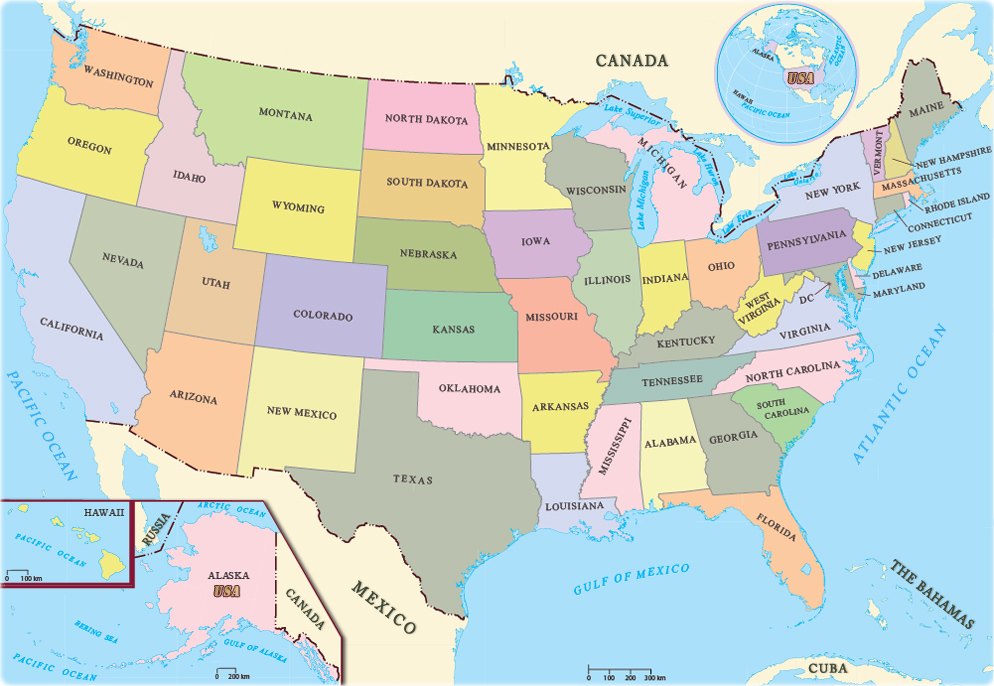
The United States of America (USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. The third-largest country in the world by land and total area, the U.S. consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territories, nine Minor Outlying Islands and includes 326 Indian reservations. It shares land borders with Canada to its north and with Mexico to its south and has maritime borders with several other countries.
The United States national government is a federal presidential constitutional republic and liberal democracy with three separate branches of government: legislative, executive, and judicial; this governmental structure is designed to maintain a system of checks and balances among the branches. It has a bicameral national legislature composed of the House of Representatives, a lower house based on population; and the Senate, an upper house based on equal representation for each state. Many policy issues are decentralized at a state or local level, that can vary by jurisdiction. However, they must conform with and are subordinate to the Constitution.
A developed country, the United States has the highest median income per capita of any non-microstate and possesses by far the largest amount of wealth of any country. The American economy accounts for over a quarter of global GDP and is the largest nominally. It ranks among the highest in the world in the international measures of human development, income, wealth, economic competitiveness, productivity, innovation, human rights, and education. The United States is a founding member of the United Nations, the World Bank, the International Monetary Fund, the Organization of American States, NATO and WHO and is a permanent member of the United Nations Security Council. It is globally recognized as the world’s foremost political, cultural, economic, military and scientific power, and wields considerable global influence. It is one of the world’s nuclear-weapon states.
Border Facts
The United States borders Canada in the north and Mexico in the south. Also known as the International Border, the Canada-United States border is the world’s longest land border that is shared by two countries. In addition to its land border, the United States has a maritime border shared with Russia, Cuba, and the Bahamas. The delineation of the United States’ borders was achieved through numerous treaties that the country signed over the course of its history.
US Border-Canada Border is the longest international border in the world. The terrestrial boundary (including boundaries in the Great Lakes, Atlantic, and Pacific coasts) is 8,891 km long. The land border has two sections: Canada’s border with the contiguous United States to its south, and with the U.S. state of Alaska to its west. The bi-national International Boundary Commission deals with matters relating to marking and maintaining the boundary, and the International Joint Commission deals with issues concerning boundary waters. The agencies responsible for facilitating legal passage through the international boundary are the Canada Border Services Agency (CBSA) and U.S. Customs and Border Protection (CBP).
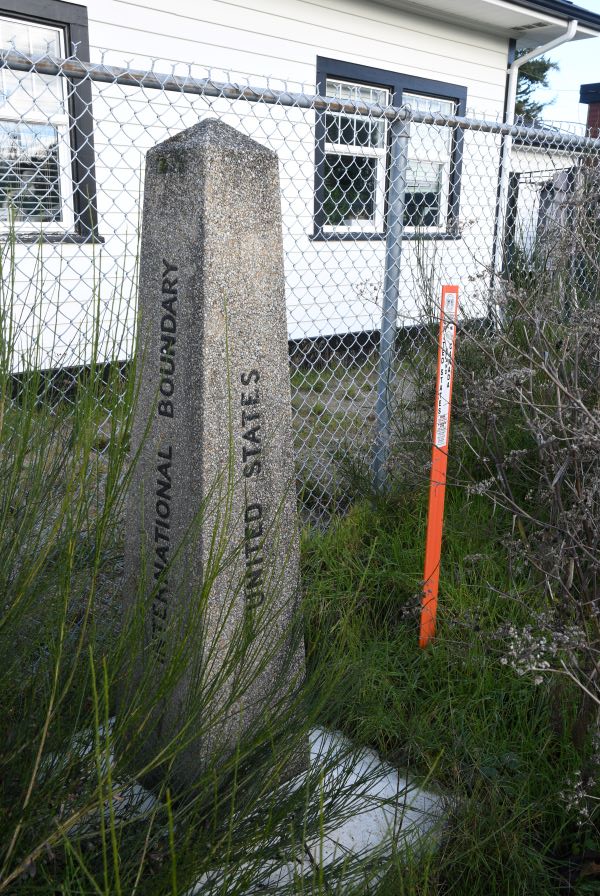
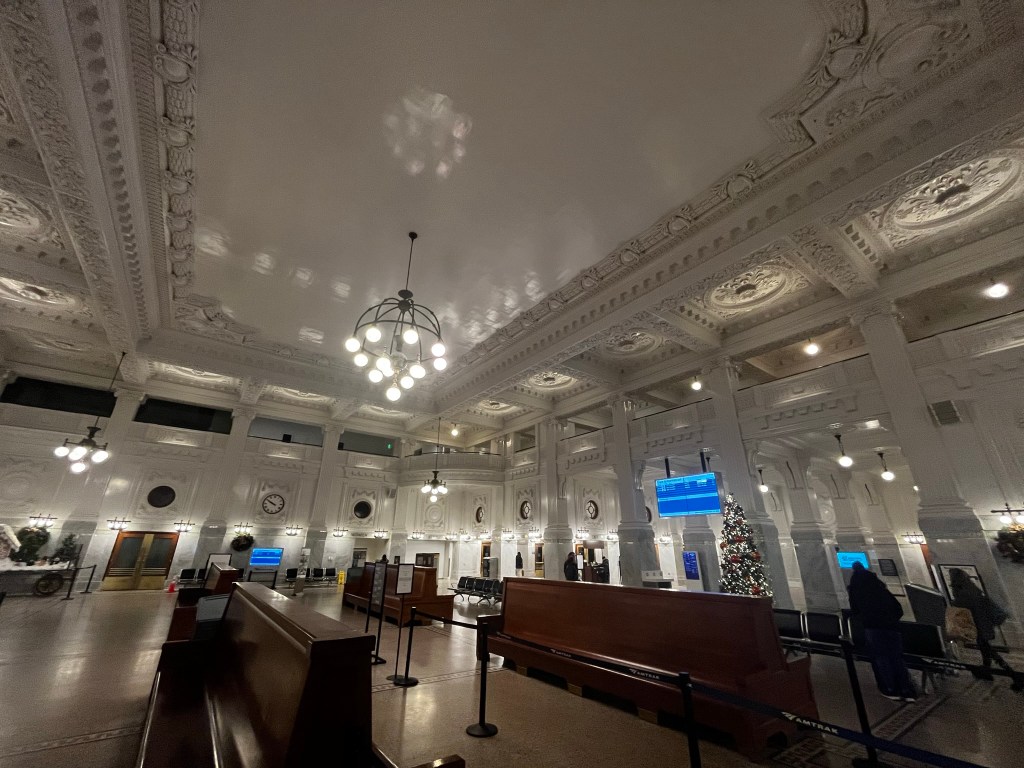



Travelling north the US border controls occur at the border at Blaine, Washington as there are a number of intermediate stops north of Seattle. Canadian customs and immigration inspection takes place at the Pacific Central Station in Vancouver.
The length of the terrestrial boundary is 8,891 km, of which 6,416 km is with the contiguous 48 states, and 2,475 km with Alaska. Eight out of thirteen provinces and territories of Canada and thirteen out of fifty U.S. states are located along this international boundary.
The Treaty of Paris of 1783 was the first treaty that established the boundary between the 2 countries, whereas the London Convention of 1818 established the border very much as it exists today. The International Boundary Survey (or, the “Northern Boundary Survey” in the US) role is maintaining the survey and mapping of the border; maintaining boundary monuments and buoys; and keeping the border clear of brush and vegetation for 6 m.
The 49th Parallel is the single fact most closely associated with the Canada – US border. This part of the border from the Lake of the Woods to the Rockies was set in October 1818, and was later extended all the way to the Pacific Coast. East of Minnesota’s Northwest Angle the border is more complex following lakes and rivers and other physical features until it reaches the Atlantic Ocean.
Currently there are 119 legal land border crossings between the United States and Canada, 26 of which take place at a bridge or tunnel. Only 2 of the 119 crossings are one-way.
There are 39 railroads that cross the U.S.–Canada border, nine of which are no longer in use. Eleven of these railroads cross the border at a bridge or tunnel.
Only three international rail lines currently carry passengers between the U.S. and Canada. At Vancouver’s Pacific Central Station, passengers are required to pass through U.S. partial pre-clearance and pass their baggage through an X-ray machine before being allowed to board the Seattle-bound Amtrak Cascades train, which makes no further stops before crossing the border at Blaine, Washington, where the train stops for another CBP inspection.

Pre-clearance facilities are not available for the popular Adirondack (New York City to Montreal) or Maple Leaf (New York City to Toronto) trains, since these lines have stops between Montreal or Toronto and the border. Instead, passengers must clear customs at a stop located at the actual border. It is often written that this is the longest undefended border. The border is however controlled remotely and by border officers.
With a border of this length, there are bound to be a number of oddities such as cross border airfields and golf courses. At some points houses are divided by the border. Given the inaccuracy of early surveying techniques and mapping there are geographical oddities. The 2 most well known ones are Point Roberts and the Northwest Angle.
Canada and the United States have one land dispute over Machias Seal Island (off the coast of Maine), and four other maritime disputes in the Arctic and Pacific. In addition there is a dispute over the status of the Northwest passage. Canada has long claimed the Northwest Passage as internal territorial waters, on the basis of a long history of native Inuit use of the waters, as well as legal arguments stemming from decades-old cases settled by the the International Court of Justice. The U.S. has long countered this claim on the basis of its interpretation of the UN Convention on the Law of the Sea (UNCLOS), a treaty which it accepts as international law but has never been ratified by Congress. Under this view, the U.S. sees the passage as an international strait connecting two large bodies of water. However, the “international strait” designation is usually only used in cases where there is a large volume of traffic transiting the strait. Currently, there is not much traffic, but traffic will likely increase as ice continues to melt. Under this international strait framework, Canada has the right to regulate most aspects of traffic in the waterway, yet cannot prohibit or restrict international shipping traffic
US – Mexico Border extends 3,145 kilometres, in addition to the maritime boundaries of 29 km into the Pacific Ocean and 19 km into the Gulf of Mexico. From the Gulf of Mexico, it follows the course of the Rio Grande (Río Bravo del Norte) to the border crossing at Ciudad Juárez, Chihuahua, and El Paso, Texas. Westward from El Paso–Juárez, it crosses vast tracts of the Chihuahuan and Sonoran deserts to the Colorado River Delta and San Diego–Tijuana, before reaching the Pacific Ocean.
Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo (1848) established the United States-Mexico international boundary. The treaty established temporary joint commissions to survey, map, an demarcate with ground landmarks the new United States – Mexico boundary. Since then there have been a series of further conventions and treaties to refine and further clarify the course of the border, the last being the1970 treaty referring to the Rio Grande and the Colorado River
The U.S. states along the border, from west to east, are California, Arizona, New Mexico, and Texas. The Mexican states along the border are Baja California, Sonora, Chihuahua, Coahuila, Nuevo León, and Tamaulipas. Among the U.S. states, Texas has the longest stretch of the border with Mexico, while California has the shortest. Among the states in Mexico, Chihuahua has the longest border with the U.S., while Nuevo León has the shortest.
There are 48 U.S.–Mexico border crossings, with 330 ports of entry. The San Ysidro Port of Entry is located between San Ysidro, California and Tijuana, Baja California. Approximately 50,000 vehicles and 25,000 pedestrians use this entry daily. In the U.S., I-5 crosses directly to Tijuana, and the highway’s southern terminus is this crossing. This is the busiest border crossing in the world.
The Wall
The Trump wall, commonly referred to as “The Wall”, is an expansion of the Mexico–United States barrier that started during the U.S. presidency of Donald Trump and was a critical part of Trump’s 2016 presidential campaign platform leading up to the year’s election. Throughout his campaign, Trump called for the construction of a border wall. He said that, if elected, he would “build the wall and make Mexico pay for it”. This of course did not happen. The U.S. built new barriers along 732 km, 79 km of which previously had no barrier. Much of the remainder consists of 9.1 m steel bollard wall where previously there had been fencing or vehicle barriers. Since 2021 building has effectively stopped.
The US-Russia Border The Russian mainland and mainland Alaska are separated by the Bering Strait measuring about 81 km.
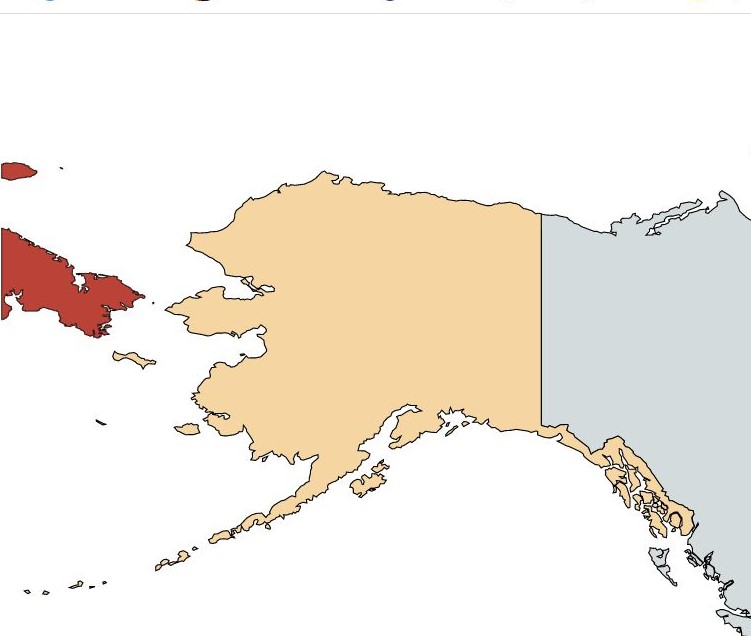
When the US purchased Alaska from Tsarist Russia, the two nations drew a line between two small islands in the Bering Sea to designate the boundary. The distance between Big Diomede, which is on the Russian side and Little Diomede on the US side, is roughly 3.9km. The border also serves as the International Date Line. In winter it is possible to walk between the islands. The US island is occupied by Inuit people whereas the Russian island is a military base.
Maritime Borders The United States has entered maritime boundary agreements with Mexico, Cuba, Venezuela, and with the United Kingdom in the Caribbean.
USA Registration Plates
Vehicle registration plates of USA, also known as licence plates, are issued by a department of motor vehicles, an agency of the state or territorial government, or in the case of the District of Columbia, the district government. Some Native American tribes also issue plates. The U.S. federal government issues plates only for its own vehicle fleet and for vehicles owned by foreign diplomats. Until the 1980s, diplomatic plates were issued by the state in which the consulate or embassy was located.












Site Navigation
In order to find your way around the site, either click on the links (text in red) or use the menus at the top and side of the pages. About leads you to the main areas of the site. The European Tripoints menu leads directly you to my visit reports whereas the Country Visits page allows you to choose which country to look at first. Many photos are also links to further information, reports and analysis.
Mobile User Advice
Tables display correctly when holding your mobile horizontally.
To access the links to other pages please click on the 3 horizontal dots at the bottom of the page.