Spain (officially the Kingdom of Spain) is a country in Southwestern Europe with 5 small areas of territory along the northern coast of Morocco. The African enclaves of Ceuta, Melilla, and Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera and additional small islands off the coast makes Spain the only European country with a land border with an African nation. Its territory also includes two archipelagos: the Canary Islands off the coast of North Africa, and the Balearic Islands in the Mediterranean Sea. The country’s mainland is bordered to the south and east by the Mediterranean Sea except for a small land boundary with Gibraltar; to the north and northeast by France, Andorra, and the Bay of Biscay; and to the west and northwest by Portugal and the Atlantic Ocean respectively.
With an area of 505,990 km2, Spain is the largest country in Southern Europe, the second-largest country in Western Europe and the European Union, and the fourth-largest country by area on the European continent. Spain is a major developed high income country, a secular parliamentary democracy and a parliamentary monarchy. It is a member of the United Nations (UN), the European Union (EU), the Eurozone, the Council of Europe (CoE), the Organization of Ibero-American States (OEI), the Union for the Mediterranean, the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD), Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE), the Schengen Area, the World Trade Organization (WTO) and many other international organisations. It is a de facto member of the G20 Group.
Border facts: Spain has a total land border of 1928 km long that is shared by five countries: Morocco, Andorra, France, Portugal, and Gibraltar. The country also borders the Mediterranean Sea, the Bay of Biscay and the Atlantic Ocean. Portugal borders the country in the west, Gibraltar in the south, France and Andorra in the northeast while Morocco is bordered by Spain’s autonomous cities of Melilla and Ceuta and other small areas of land and islands. Additionally, the country has an enclave known as Llivia that is situated inside France. My report on Llivia is here.
Spain – Andorra border is 64 km long between the south of Andorra and Catalonia, northern Spain. Because both Spain and Andorra are situated in the same watershed, travel is easier (roads are better) than travel between Andorra and France. The most used languages of Andorra are also Catalan and Spanish. The border begins in the west at the Andorra-France-Spain tripoint ADESFRw. It then follows a generally south-eastern direction, later turning northeast to the eastern Andorra-Spain-France tripoint ASESFRe. The border between the two countries goes through high mountain areas in the Pyrenees.
It is the outer border of the EU, as Andorra is not part of the EU, nor Schengen and therefore there are full passport and custom checks. The main border crossing is La Seu d’Urgell – Sant Julia de Loria, my report here. There are other roads crossing the border to Spain – one to the pene enclave of Os de Civís (my report here) and one via Port de Cabús (although this is a challenging rural track on the Spanish side of the border open only between June and October, details here). There are currently no rail links although one is planned, details here.
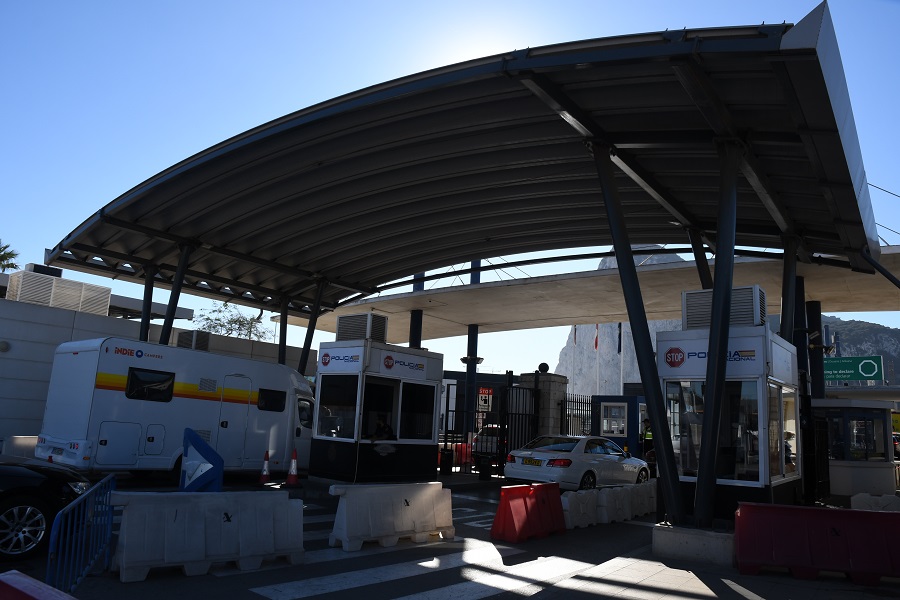
Spain – Gibraltar border is 1200 metres long and one of the shortest in the world. The status of Gibraltar is a point of contention between Spain and the United Kingdom. In 1910 the British built a fence which according to them was 1 meter inside their part of the neutral territory. The Spanish later contested it was actually 2 meter inside their territory. There is disagreement about where the border should be with the British arguing that their ownership of the 800 m strip of the isthmus is based on the initial position of border forts and de facto ownership. The northern half of the neutral territory was also taken over by Spain in the 1960s, during dictator Francisco Franco’s regime, and now forms an integral part of the Spanish municipality of La Línea de la Concepción. Between 1969 and 1982 the border was closed by Franco, in 1982 local pedestrians were allowed to cross whilst in 1985 the border was opened to vehicular traffic as well. Nowadays 12000 citizens commute to work in Gibraltar each day. My report on Gibraltar is here.
Spain – France border is 656 km long but interrupted for 63.7 km by Andorra. The border is marked by 602 (main) border markers.


The France–Spain border was formally defined in 1659, with the signing of the Bayonne Treaties of 1856 and 1868. It separates the two countries from Hendaye and Irun in the west, running through the Pyrenees to Cerbère and Portbou on the Mediterranean Sea. Shortly after the start of the western border, following the course of Bidasoa River, Pheasant Island located in the middle of the river has a particular border regime: the island is a condominium whose sovereignty is shared between the two countries determined by if it is the first or the second half of a year. Another anomaly is Llívia, a town of Cerdanya, province of Girona, Catalonia, Spain. It is an exclave of Spain and an enclave of France, within the French territory (Pyrénées-Orientales département). In 1659, the Treaty of the Pyrenees ceded the comarques of Roussillon, Conflent, Capcir, Vallespir, and northern Cerdanya (“Cerdagne”) to the French crown.

Llívia did not become part of the French kingdom as the treaty stipulated that only villages were to be ceded to France, and Llívia was considered a city and not a village due to its status as the ancient capital of Cerdanya.
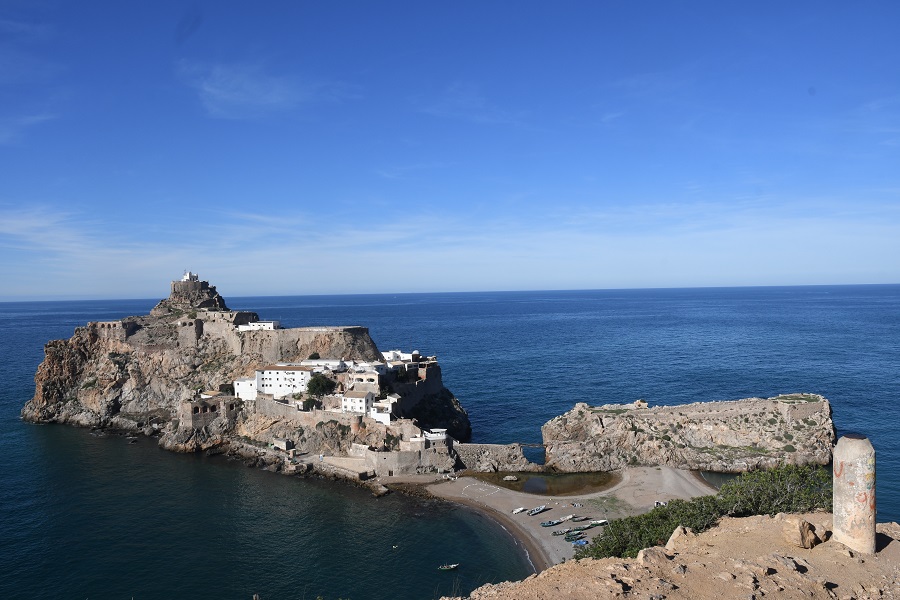
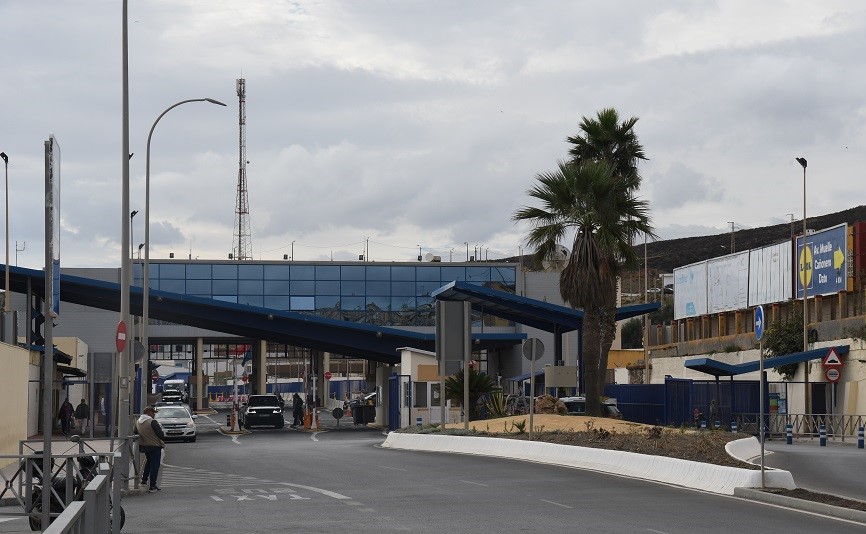
Spain-Morocco border is through its exclaves in North Africa (Ceuta and Melilla, and the peninsula of Peñón de Vélez de la Gomera) which trace their Spanish past to the 15th century. Coveted by Morocco, they have long been a flashpoint in diplomatic relations with Spain. Madrid asserts that both territories are integral parts of Spain and have the same status as the semi-autonomous regions on its mainland. Increasingly Ceuta and Melilla’s heavily fortified borders have come under pressure from African migrants seeking a better life in Europe. Human rights groups and the European Union have raised concerns with Madrid about the deportation of illegal immigrants. In addition to these exclaves Spain also claims ownership of Isla Perejil, the Alhucemas Islands, Alboran Island and small islote de La Nube and finally the Chafarinas Islands.

Spain-Portugal border is referred to as “The Stripe” (Spanish: La Raya). It is one of the oldest borders in the world. The current demarcation is almost identical to that defined in 1297 by the Treaty of Alcañices. The Portugal–Spain border is 1,214 km long, and considered the longest uninterrupted border within the European Union. The border is not defined for 18 km between the Caia river and Ribeira de Cuncos, because of the disputed status of Olivenza/Olivença, which has been disputed between the two countries for two hundred years. According to Spain, the region is part of the country’s Extremadura autonomous community, while Portugal believes the town to be part of its Province of Alto Alentejo. Nonetheless, the administration of Olivenza is done by the Spanish government. The region covers an area of 751 km2 and has an estimated population of 11,512 people. Portugal claimed the region since 1297 but had the sovereignty of the town taken by Spain in the aftermath of the 17th century War of Oranges and the signing of the 1801 Treaty of Badajoz.
Portugal and Spain signed the Schengen Agreement in June 1991 which came into effect on 26 March 1995, making Portugal and Spain part of the Schengen area and thus the border then became an Open border. The recent COVID 19 pandemic has led to the border being closed for 4 months.
Spanish Registration Plates


Spanish Passport Stamps



Spanish Tripoints

| NUMBER | NAME | COUNTRIES | TYPE | COORDINATES | Notes/LINKS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
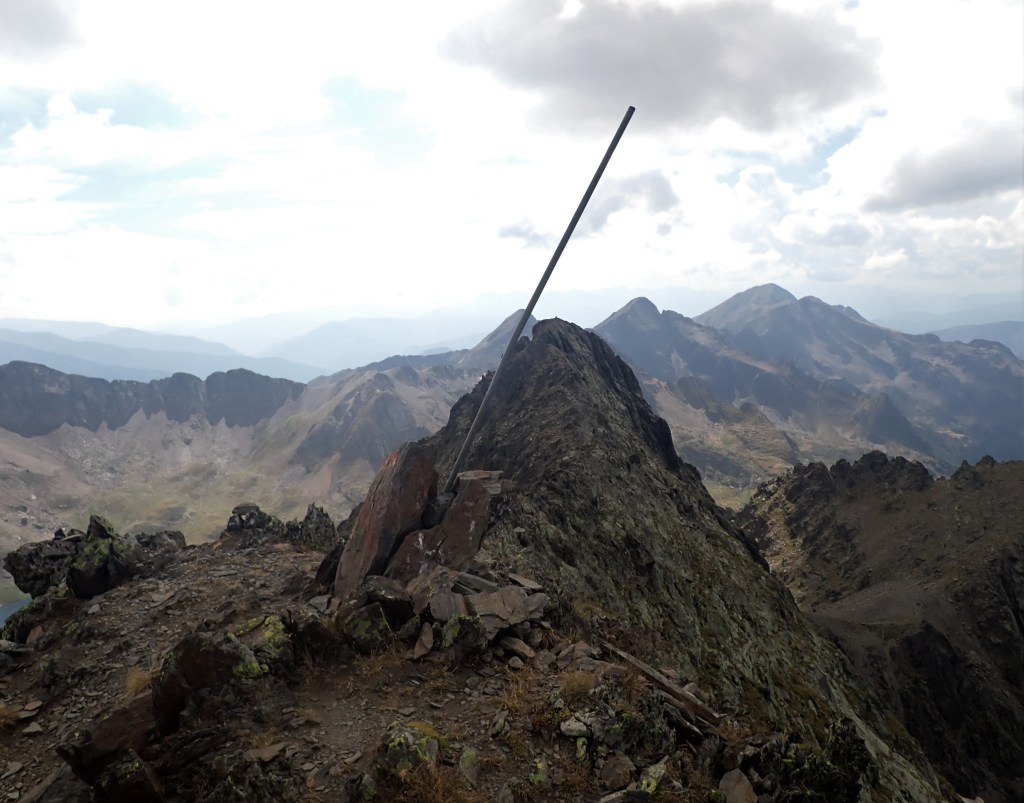
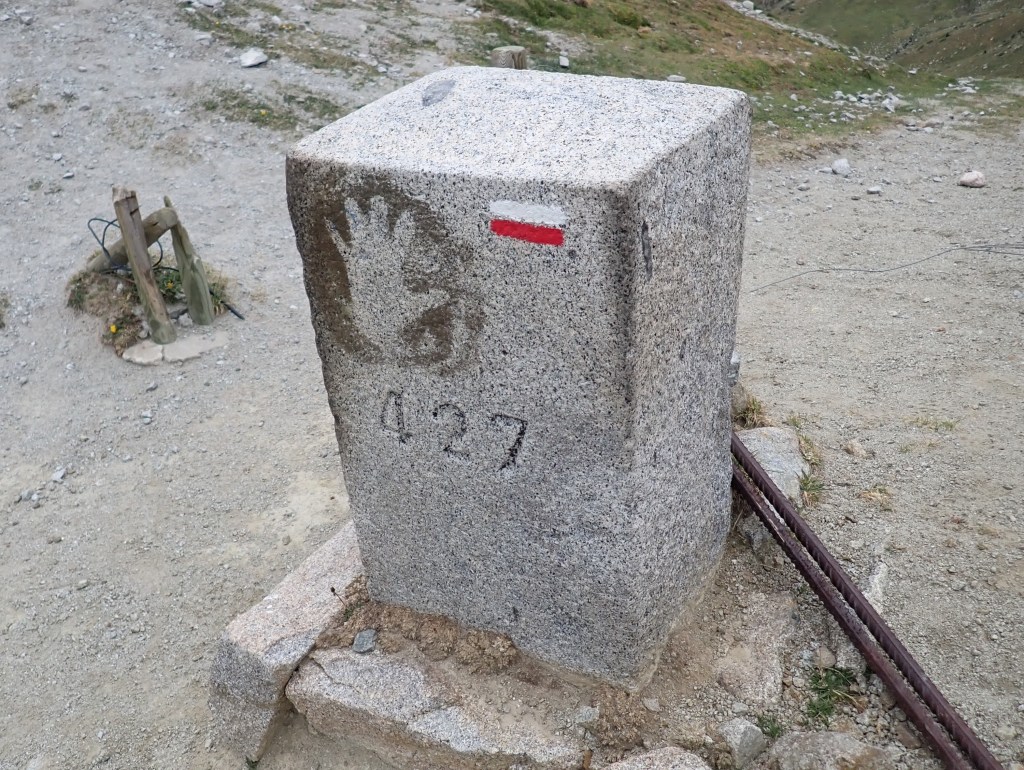
| 1 | ADESFRe | Andorra – France – Spain (E) | Dry | 42°30’09″N 01°43’28″E | The Portella Blanca d’Andorra or Coll d’Engaït (2515m) is a mountain pass where the boundaries of Andorra, Spain and France meet. It also forms the administrative boundary of Encamp , Lles de Cerdanya , and Porta. At the top of the pass there is border marker #427 which is taken to mark the tripoint. Both Andorra and Spain record the tripoint as being slightly further south at an unmarked col however. Berns (2004) |
| 2 | ADESFRw | Andorra – France – Spain | Dry | 42°36’07″N 01°26’32″E | The tripoint is located at the summit of Pic de Médecourbe (2914m). From the Collada dels Estanys Forcat (2745 m) there is a short but steep and faint path up to the narrow top. Berns (2004) |
Tripoint Gallery

Site Navigation
In order to find your way around the site, either click on the links (text in red) or use the menus at the top and side of the pages. About leads you to the main areas of the site. The European Tripoints menu leads directly you to my TP visits reports whereas the Country Visits page allows you to choose which country to look at first
Mobile Advice
Tables display correctly when holding your mobile horizontally.
To access the links to other pages please click on the 3 horizontal dots at the bottom of the page